Percussion instruments have been captivating musicians and audiences for centuries. With their diverse range of sounds, these instruments add depth, texture, and excitement to musical compositions across genres.
In this blog post, we embark on a journey through the world of percussion. We will explore a wide variety of percussion instruments, each with its own unique characteristics and cultural significance.
Whether you’re a seasoned musician, a curious music enthusiast, or simply someone looking to broaden their musical horizons, this comprehensive guide will introduce you to the rich tapestry of percussion instruments found around the globe.
Through this exploration, we hope to deepen your appreciation for the role that percussion plays in shaping the rhythm, energy, and emotion of music.
Contents
Timpani
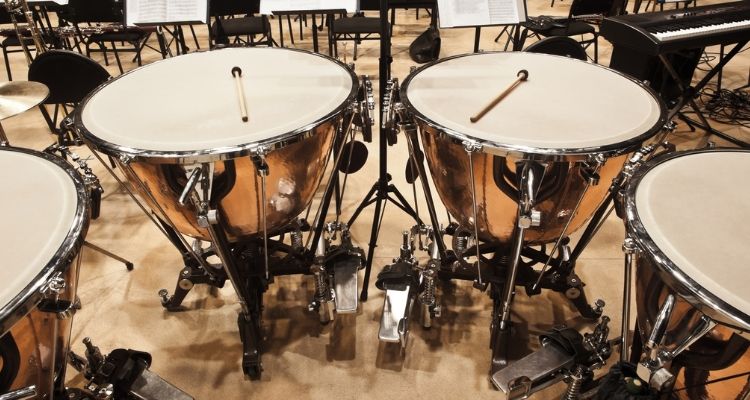

The timpani, also known as kettle drums, is a percussion instrument that consists of a set of large, tuned drums with a bowl-shaped body and a drumhead stretched over the top. They are played using mallets.
Timpani holds a significant role in music, particularly in orchestras and symphonic compositions. They provide the foundation for rhythm and add depth and power to the overall sound.
With their deep, resonant tones, timpani create dramatic impact, accentuate climactic moments, and emphasize musical transitions. The timpanist’s skillful control of dynamics helps them to shape the musical narrative, making the timpani an indispensable element in orchestral and ensemble performances.
Xylophone

The xylophone holds a central place among percussion instruments. It is a percussion instrument consisting of a series of wooden bars that are struck with mallets to produce sound. Each bar is tuned to a specific pitch, allowing the xylophone to create melodies.
Xylophones serve in many capacities such as solos, accompaniment roles within orchestras or bands. Its bright and vibrant tones add a distinctive timbre to musical arrangements, creating an enchanting and playful atmosphere.
The xylophone has a rich history and cultural significance in various parts of the world, ranging from traditional African and Indonesian music to orchestral compositions.
The xylophone’s versatility allows it to be featured in a wide range of genres, from classical to contemporary, making it a cherished instrument that brings joy, rhythm, and melody to music compositions.
Marimba
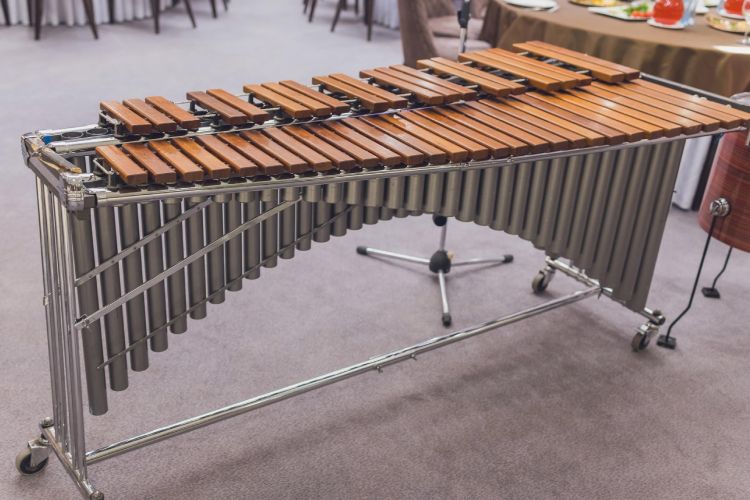

The marimba and xylophone are both percussion instruments with similar appearances, but there are some key differences between them, mainly surrounding the sound they produce.
The xylophone has bars made from a harder wood or synthetic materials like fiberglass or plastic. This gives the xylophone a bright and piercing tone with quick decay. It is known for its crisp and percussive sound.
On the other hand, the marimba has larger wooden bars made from softer wood, such as Honduras rosewood or padauk. These softer bars create a warmer and more resonant sound with a longer sustain. The marimba’s tone is mellower and richer compared to the xylophone.
The size of marimba can vary, but some are so large they require multiple people to play them!
The marimba’s unique warm timbre and expressive range allow it to evoke emotions, create captivating melodies, and contribute to the sonic landscape of music in a truly remarkable way.
Glockenspiel
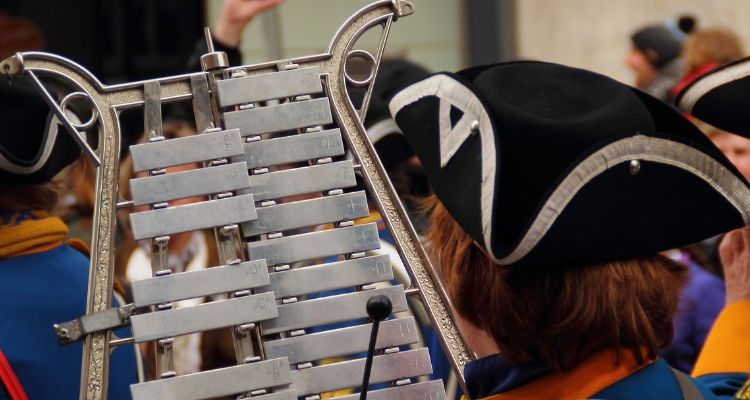

The glockenspiel is a percussion instrument that is composed of metal bars that are arranged in a chromatic scale and played with mallets. It produces clear and bell-like tones, akin to a miniature xylophone.
Its bright, bell-like tone sets it apart making it a unique addition to orchestras or ensemble performances.
Unlike its counterparts, the Glockenspiel’s metallic bars provide an enchanting higher pitch sound which is often incorporated into festive music or occasions. Renowned composers such as Beethoven and Mozart have used this versatile instrument to add depth and rich harmonic notes to their compositions.
Cymbals
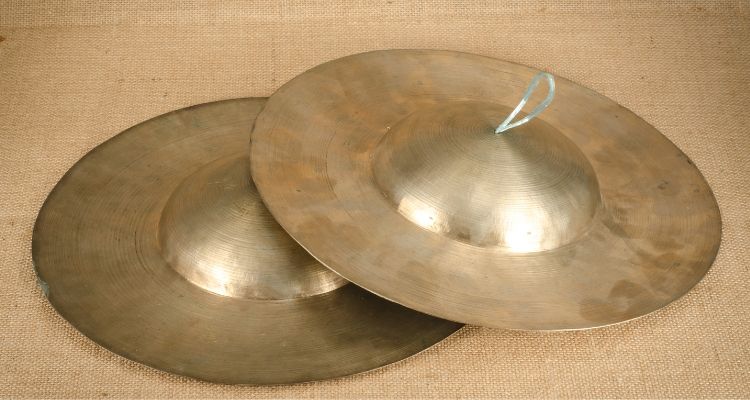

Cymbals are a famous type of percussion instrument that produce sound when struck together or with a drumstick. They are made of a bronze alloy and are found in almost every style of music.
In terms of their use in percussion, they are commonly found in orchestras and marching bands. They add shimmering and explosive accents to music, creating an impactful and dynamic sound.
Cymbals are essential components of any percussion ensemble and are often used to mark transitions or emphasize certain moments in a musical piece.
Their distinct sound adds depth and excitement, and the powerful presence of cymbals is hard to ignore.
Triangle
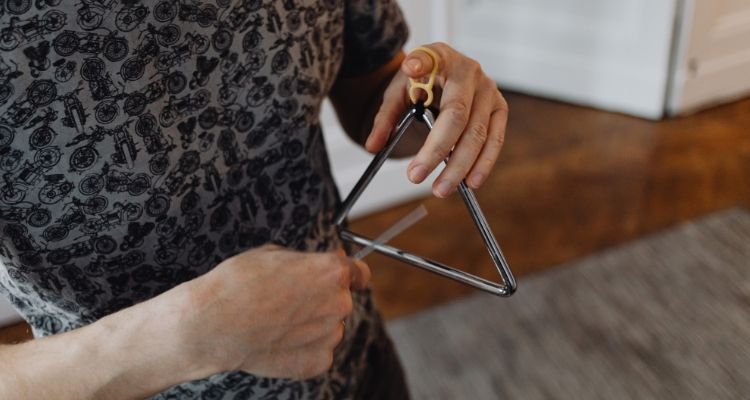

The triangle is a small percussion instrument made of metal and it produces a distinctive high-pitched sound when struck with a beater.
The player holds the triangle by its string and strikes it with a beater to mark certain beats or provide a subtle, sparkling effect in compositions.
The triangle is commonly used in orchestras, concert bands, and other musical groups to add color and texture to the music. Its gentle yet clear, ringing tone cuts through the sound of other instruments.
Its use can be found in many orchestral works, symphonies, and various musical ensembles, adding an element of sparkle and color to the overall sound palette.
Snare Drum
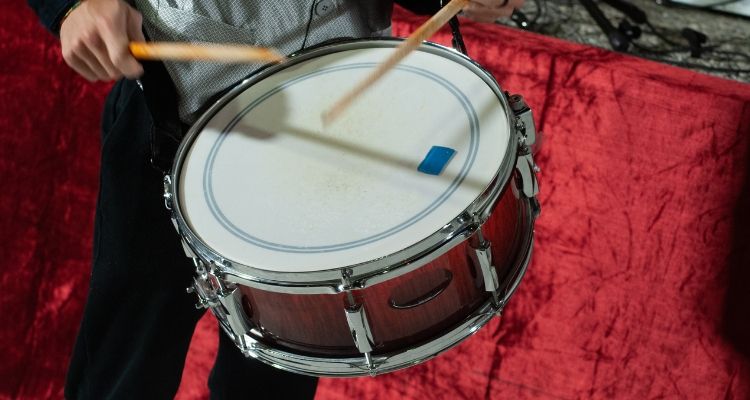

The snare drum is a versatile and essential instrument in the percussion family. It is characterized by its distinctive tight, crisp sound produced when struck with drumsticks or brushes.
The snare drum consists of a cylindrical shell made of wood or metal, with a drumhead stretched tightly over each end. The top head, commonly known as the batter head, is played with sticks to create sharp beats and rhythms.
On the bottom head lies a set of wires called snares that give the drum its unique buzzing sound.
Snare drums are used in various musical genres, from orchestral symphonies to marching bands, jazz ensembles to rock bands.
With its distinct timbre and ability to produce different tones depending on playing techniques, such as rimshots or ghost notes, the snare drum offers endless creative possibilities for percussionists.
Steelpan
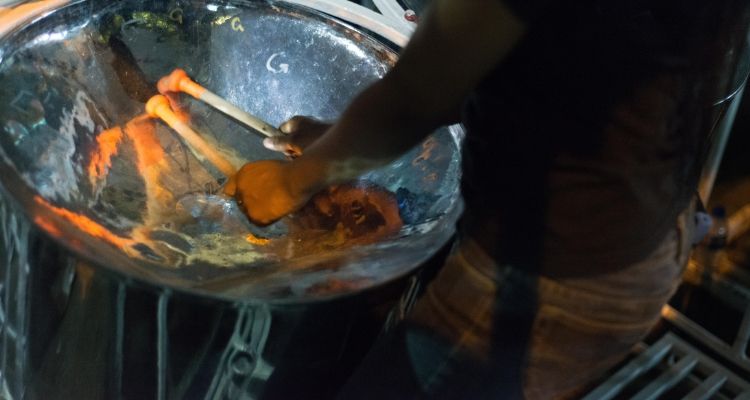
Originating from Trinidad and Tobago, the steelpan is a melodic percussion instrument made from a steel oil drum that is carefully hammered into different sections to create varying pitches.
The steelpan holds great significance in music as it is deeply rooted in the cultural heritage of the Caribbean. It offers a vibrant and infectious sound that captures the essence of Caribbean rhythms, such as calypso, soca, and reggae.
The sound of the steelpan is bright and resonant, making it perfect for adding rhythm and melody to an ensemble. It can be played solo or as part of a larger steelband, where multiple players perform together to create intricate melodies and harmonies.
With its vibrant sound and distinct cultural heritage, the steelpan has gained worldwide recognition as one of the most iconic percussion instruments and an iconic symbol of celebration, joy, and cultural identity in global music.
Bass Drum
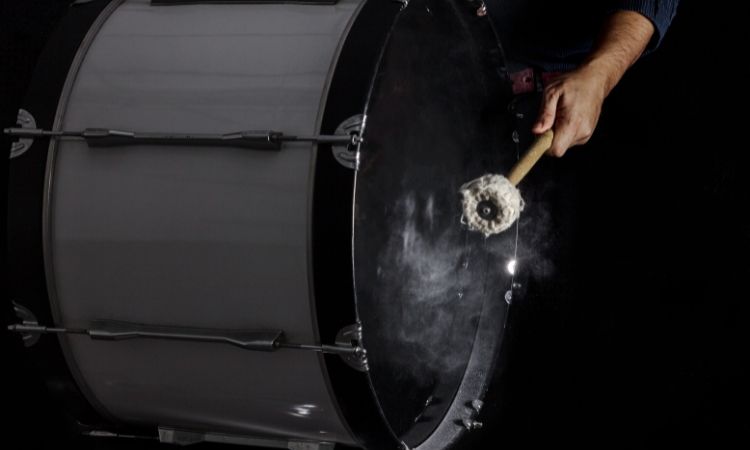

The bass drum is a powerful and booming percussion instrument that adds depth and impact to a musical ensemble.
In orchestral ensembles, the player strikes the head with a mallet to produce its characteristic deep and resonant sound. With its low-pitched tones, the bass drum serves as the foundation for the rhythm section.
Its thunderous presence commands attention and sets the pulse for many orchestral and symphonic arrangements, as well as in marching bands.
Bongo Drum
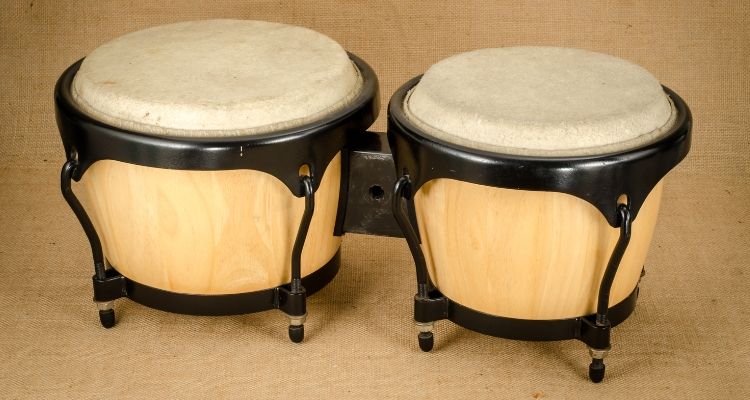

The Bongo Drum is a percussion instrument that originated in Cuba. It consists of two small drums, one slightly larger than the other, attached to each other. The drums are typically made from wood or fiberglass and have animal skin heads.
Bongo drums are often used in Latin American and Afro-Cuban music genres. They add a distinct rhythm and flair to an ensemble, making them popular in salsa, merengue, and rumba bands.
The player strikes the drums with their fingertips or palms to create different pitches and rhythms. They produce rich and vibrant tones.
With its compact size and versatile sound, the Bongo Drum is a favorite among drummers and percussionists alike. Its lively beats can be heard in both traditional songs and modern compositions.
Djembe Drum
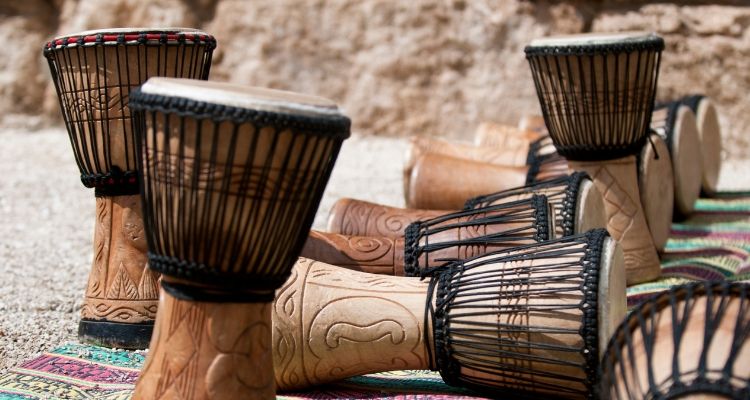

The Djembe Drum is a versatile and dynamic percussion instrument that originated in West Africa. It has a goblet-shaped body, made from carved wood and covered with animal skin.
The player uses their hands to strike the drumhead, producing different tones by hitting various areas of the surface.
The Djembe Drum is known for its powerful sound and rhythmic versatility. It can produce a wide range of tones, from deep bass to sharp slaps, allowing it to be used in many musical genres.
In West African culture, the Djembe Drum holds great significance as a means of communication and expression during ceremonies and celebrations.
Today, the Djembe Drum has gained popularity worldwide for its vibrant sound and infectious rhythms. It is often used in drum circles or as an accompaniment to other instruments in both traditional and contemporary music settings.
Conga Drums
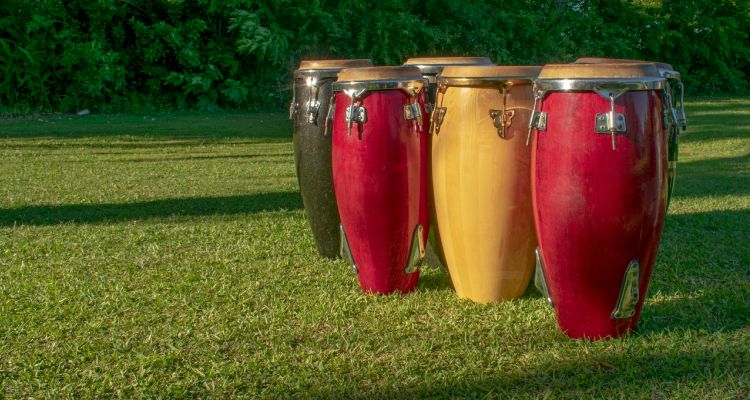

Congas are a type of drum that originated in Afro-Cuban music and have since become an integral part of various musical genres worldwide.
Consisting of tall, narrow drums with tapered bodies and animal hide drumheads, congas produce rich, resonant tones.
Played with the hands or with drumsticks, conga drums have a long history dating back to African traditions brought over during the slave trade.
With their deep roots in African and Latin American traditions, congas play a significant role in creating the infectious grooves and polyrhythms that define genres such as salsa, rumba, and Afro-Cuban jazz.
They are also prominent in contemporary music styles like Latin pop, fusion, and world music, adding depth, energy, and an undeniable primal element to compositions.
Cajon Drum
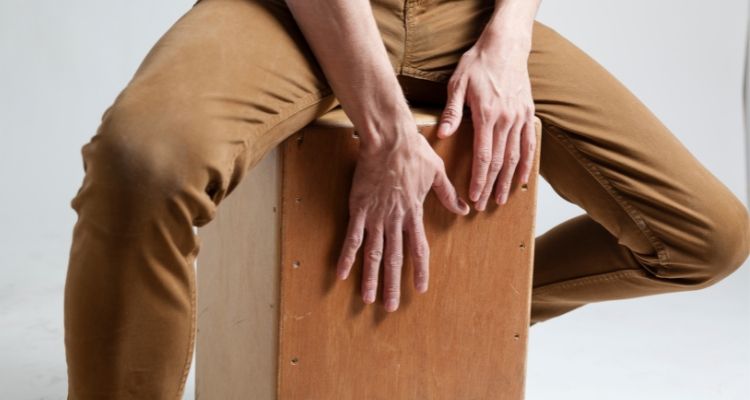

The Cajon drum is a versatile percussion instrument that originated in Peru. It is made of plywood or solid wood and has a distinctive box-like shape.
The player sits on the top of the Cajon drum and strikes different areas of the playing surface with their hands or specialized brushes to produce sound.
This popular instrument offers a wide range of tones, from deep bass to snappy high-pitched notes. By adjusting where and how they strike the surface, players can create various sounds resembling those produced by a full drum kit.
The Cajon drum is widely used in different genres such as flamenco, Latin American music, pop, rock, and jazz.
Its portable size makes it easy to carry around for performances or jam sessions. Additionally, it serves as an excellent alternative for situations where space or volume restrictions prevent using other larger drums.
Tambourine
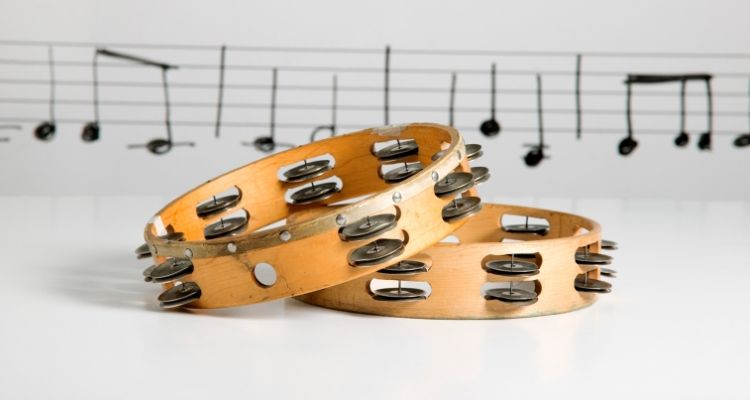

The tambourine is a famous percussion instrument that is often used in various musical genres, from folk to rock and everything in between. It consists of a circular frame made of wood or metal with jingles attached to the sides.
To play the tambourine, you hold it in one hand and strike or shake it with your other hand. The jingles create a distinctive sound that adds texture and rhythm to music.
In addition to producing rhythmic patterns, tambourines can also be used for accenting certain beats or creating special effects.
The tambourine is a fun instrument that brings energy and excitement to any piece of music. Its vibrant sound and easy playability make it popular among musicians of all levels of experience.
Castanets
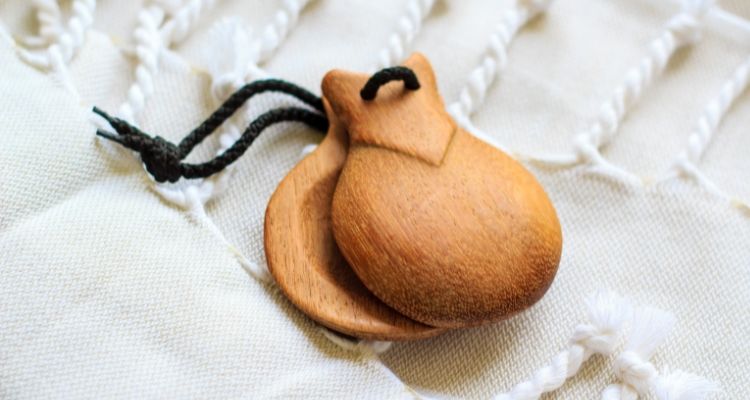

Castanets are percussive instruments that are made up of a pair of concave shells, typically made from wood or bone. They are held in both hands and struck together to produce a clicking or rattling sound.
Castanets are commonly used in Spanish and flamenco music, adding a distinctive rhythmic element to the ensemble. The player uses their thumb and fingers to rapidly open and close the shells, creating different pitches and accents.
Castanets can be played solo or as part of an ensemble, providing a lively and vibrant percussion sound.
Maracas
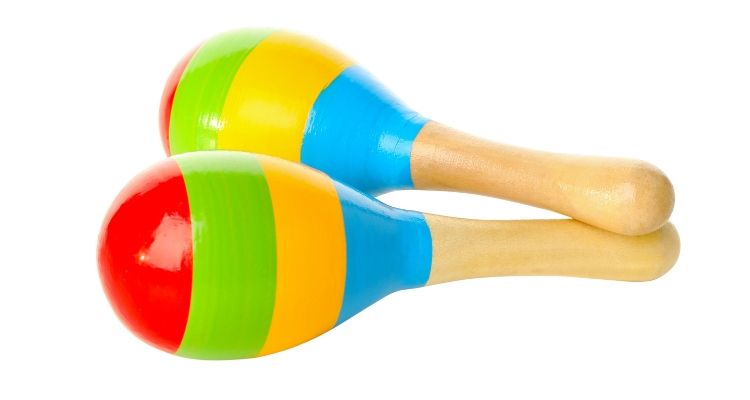

Maracas are percussion instruments that originated in Latin America. They consist of a pair of hollow gourds or shells, usually made from dried calabash fruit, attached to handles.
When shaken, the seeds or beads inside the maracas create a rhythmic rattling sound. Maracas are often used in traditional Latin American music and can be found in various sizes and shapes.
These instruments are played by holding one handle in each hand and shaking them to produce different rhythms and tones. The intensity and speed of the shaking determine the volume and pitch of the sound produced.
Maracas add a vibrant and lively element to musical ensembles, creating a distinctive percussive rhythm that complements other instruments such as drums, guitars, or pianos.
In addition to their use in Latin American music styles like salsa, merengue, or cumbia, maracas have also become popular in various genres around the world. They are commonly used in jazz bands, pop songs, and even some classical compositions.
Woodblock
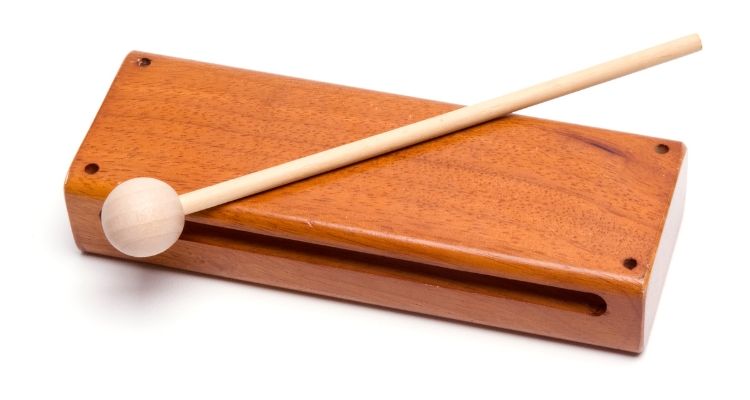

The woodblock is a percussion instrument that is often used in orchestras and other musical ensembles. It consists of a piece of hollowed-out wood that is struck with a mallet to produce sound.
The size and shape of the woodblock can vary, but it typically has a rectangular or cylindrical shape.
When the woodblock is struck, it creates a sharp and resonant tone. The sound produced by the woodblock can be loud and distinct, making it ideal for adding accents and rhythms to music.
Woodblocks have been used in various cultures throughout history and are found in traditional music from around the world.
The woodblock’s simplicity, clarity, and ability to punctuate musical phrases make it a valuable tool for creating accents, cues, and rhythmic interest in musical arrangements.
Cowbell
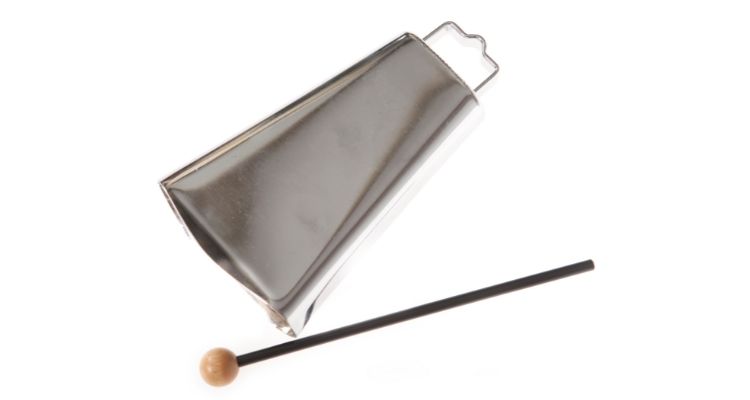

A cowbell is a popular percussion instrument that is played with a drumstick or a mallet. Cowbells are commonly used in various genres of music, including rock, Latin, and Afro-Cuban.
In music, cowbells are primarily used to add a distinct rhythmic element and enhance the overall groove of a composition. They provide a bright and penetrating sound that cuts through the mix, adding emphasis and drive to the rhythm section.
In rock music, cowbells are often played in a repetitive pattern to create an infectious beat and contribute to the energy of the song. The iconic cowbell intro in “Don’t Fear the Reaper” by Blue Öyster Cult is a classic example of its use in rock music.
In Latin and Afro-Cuban music, cowbells play a crucial role in establishing the clave rhythm. By playing specific rhythms on the cowbell, musicians create syncopated patterns that serve as a guide for other instruments and dancers.
The cowbell’s distinctive sound and versatile nature make it a useful instrument in various musical styles, providing rhythmic interest, accentuation, and a touch of character.
Guiro
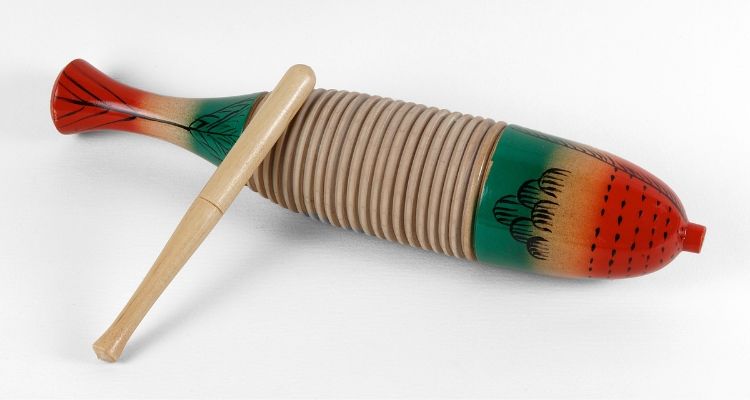

The guiro is a percussion instrument commonly used in Latin American and Caribbean music. It consists of a hollow, cylindrical tube made of wood or metal with ridges carved into its surface.
To play the guiro, a musician rubs a stick or scraper along these ridges, creating a rhythmic sound. The guiro’s significance lies in its ability to add texture, rhythm, and a lively quality to music.
Its distinctive and quirky sound makes it a fun addition to many styles of music, from salsa to reggae.
Handpan Drum
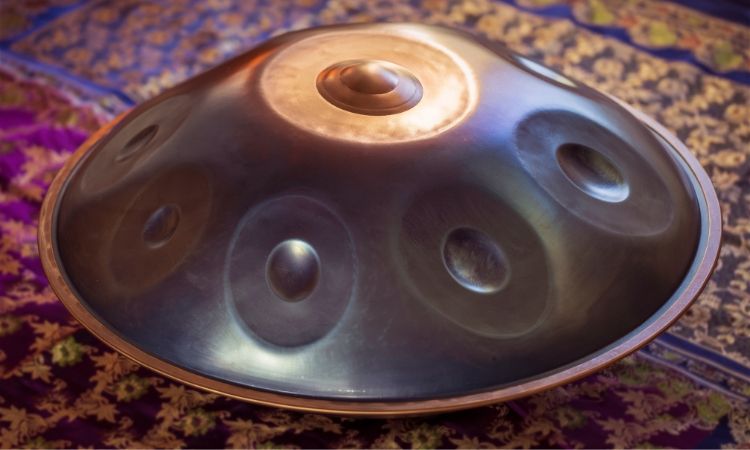

The Handpan Drum is a unique and captivating percussion instrument that has gained popularity in recent years.
It features a metal shell with a series of convex and concave indentations, creating different notes when struck or played with the hands.
The sound produced by the Handpan Drum is melodic, soothing, and reminiscent of steel drums or Tibetan bowls. It is very popular within world music, ambient music, and even meditation practices.
Playing the Handpan Drum requires gentle finger tapping or striking with soft mallets to produce its characteristic tones. The player can explore different rhythms and melodies by varying their hand positions on the drum’s surface.
Its enchanting sound resonates with people from all walks of life as it transports them to tranquil places filled with beautiful melodies.
Steel Tongue Drum
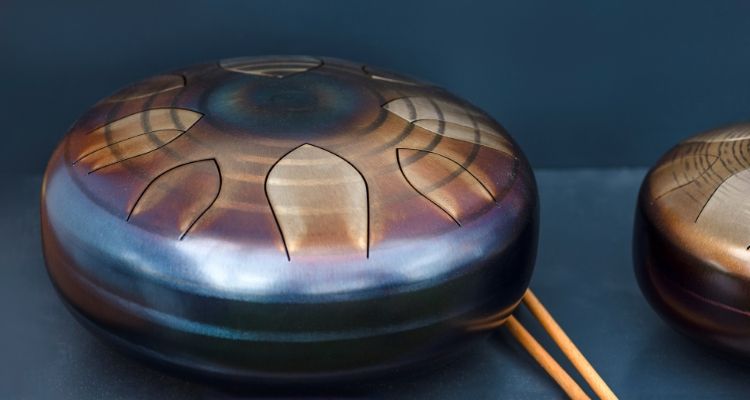

The steel tongue drum is another unique percussion instrument that produces soothing and ethereal sounds. Made from metal, this drum has several tongues or keys of varying lengths and sizes arranged in a circular pattern.
To play the steel tongue drum, one simply needs to strike the tongues with mallets, creating beautiful melodies and harmonies.
With its mesmerizing tones, the steel tongue drum can be used for various musical genres, including meditation music, ambient soundscapes, and world music. It is also gaining popularity among beginners and professional musicians alike due to its ease of playing and versatility.
Whether you are seeking relaxation or looking to add an intriguing element to your ensemble, the enchanting sounds of the steel tongue drum will mesmerize both you and your listeners.
Gongs
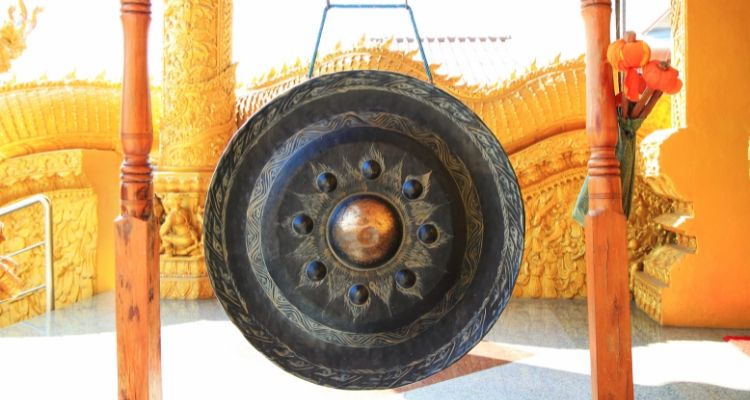

Gongs are large, circular metal plates (typically bronze) that produce deep and resonant sounds when struck. They are one of the oldest instruments in the percussion family and have been used for centuries in various cultures around the world.
Gongs are deeply rooted in the musical traditions of many cultures around the world. In Asian music, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and Indonesia, gongs play a significant role.
They are also commonly found in symphony orchestras, where they add dramatic impact and color to certain musical moments.
They are often used to accentuate climactic points, transitions, or to create a sense of grandeur. The gong’s deep and reverberating tone creates a powerful and dramatic sound.
Chimes
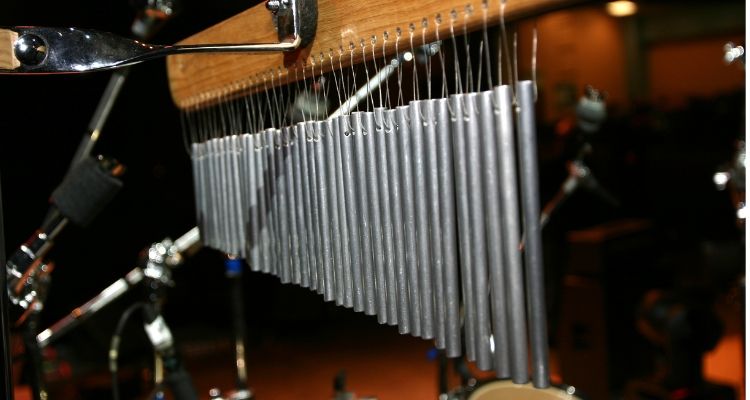

Chimes are a type of percussion instrument that produce beautiful, ringing tones. They consist of a set of metal tubes or bars suspended from a frame and are played by hitting them with mallets or striking them together.
Chimes can be made from various metals such as steel, aluminum, or brass, and they come in different sizes to create different pitch ranges. When struck, the tubes vibrate and produce rich, resonant sounds that add depth and texture to an ensemble.
Chimes are commonly used in orchestras, wind ensembles, and marching bands to provide shimmering accents and melodic lines. They are played by being struck with mallets or beaters.
Their ethereal tones create a sense of atmosphere and often evoke feelings of tranquility or mysticism.
Celesta

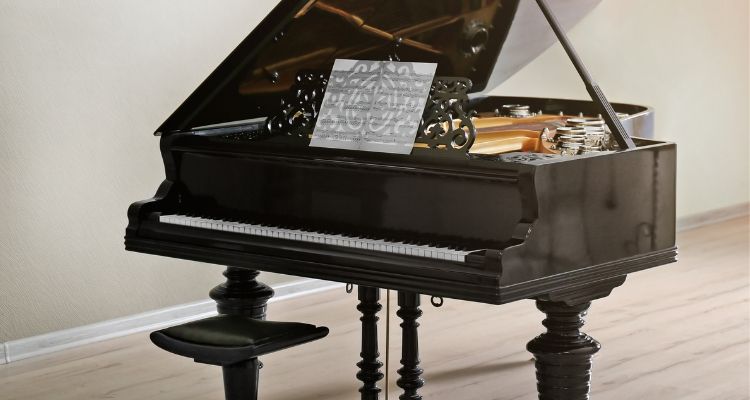
The celesta is a unique percussion instrument that produces beautiful, bell-like sounds. It consists of a small keyboard with metal bars and resonators underneath. When you press a key, hammers strike the metal bars, creating the distinct sound.
The celesta’s sound is often described as ethereal, delicate, and evocative. It has a twinkling quality that is reminiscent of music boxes or fairy tales.
The instrument’s range typically spans four to five octaves, and it is capable of producing both soft, gentle tones and bright, shimmering sounds.
The celesta’s ethereal tones have made it popular in classical music compositions, adding a magical touch to orchestral arrangements.
You might recognize its iconic melody in Tchaikovsky’s “Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy” from “The Nutcracker.” With its delicate yet enchanting sound, the celesta adds a touch of elegance and whimsy to any musical ensemble.
Piano

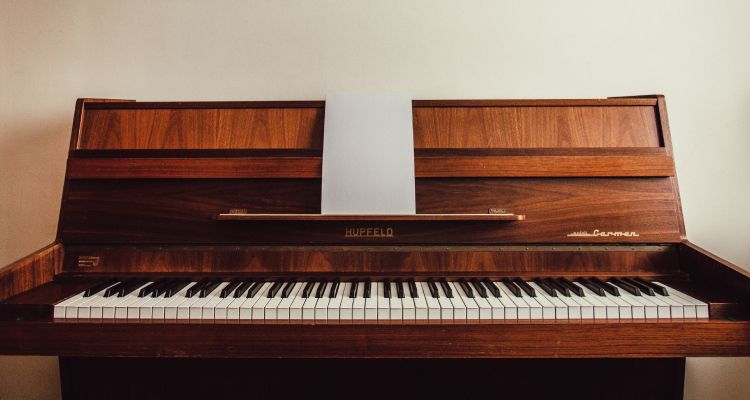
The piano is widely recognised as a beautiful melodic instrument, and interestingly it belongs to the percussion family.
It consists of a keyboard with 88 keys, which are divided into black and white notes. Each key produces a unique sound when struck by the player’s fingers.
The piano has incredible range and can produce both soft, delicate tones and powerful, resonating sounds. Its design allows for full expression and control over dynamics, making it suitable for many different musical styles.
With its timeless appeal and ability to create beautiful melodies or accompany other instruments or vocals, the piano remains an essential instrument in any ensemble or solo performance.
Tabla
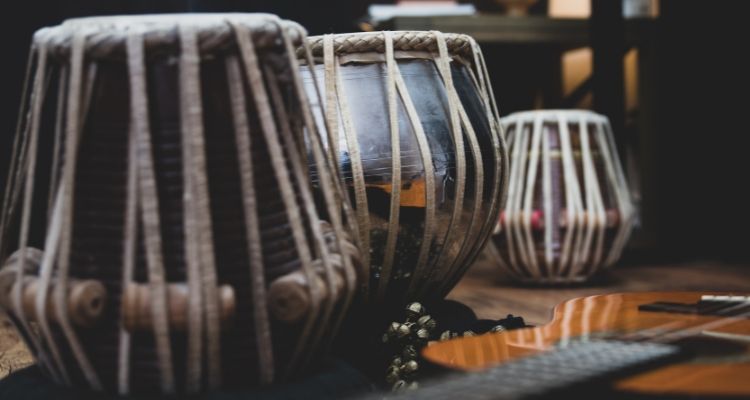

The tabla is a prominent percussion instrument originating from India. It consists of two distinct parts: the smaller drum, called the dayan, and the larger drum, known as the bayan.
The dayan is usually made from wood and has a higher pitch, while the bayan is made from metal and produces deeper tones.
Tabla players use a combination of their fingers, palms, and heels of their hands to strike the drums and produce a wide range of sounds and tones. By varying the technique and positioning of their strikes, they can create intricate rhythmic patterns and melodies.
By combining these techniques with intricate finger movements, tabla players are able to produce complex rhythms that are essential to traditional Indian music.
In addition to its important role in classical Indian music, the tabla has also gained popularity in other genres like fusion and world music.
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide has explored the fascinating world of percussion instruments, covering a diverse range of types. Each instrument brings its unique sonic qualities and cultural significance.
We have explored a wide range of instruments, each with its unique characteristics and cultural significance.
From the thunderous beats of the bass drum to the delicate chimes of the triangle, percussion instruments provide the rhythmic foundation and texture that bring music to life.
Whether in orchestras, jazz ensembles, or world music groups, percussion adds depth, excitement, and energy to musical performances.









